Mysql学习笔记
SQL语句
在数据库中直接使用sql语句,关键词部分需要用 " `` "
eg: select price from phone where name="华为"
查询
全部查询
// 全部查询
select * from users
// 只看age
select age from users
条件查询
// 条件查询
// 有一条限制语句
select * from users where age > 18
// 多条限制语句 && 与 and 是一样的
select * from users where age > 18 && price < 2000
select * from users where age > 18 and price < 2000
// || 或语句 or 与 || 一样
模糊查询
- 模糊查询
- 模糊查询 使用LIKE关键字
- %表示匹配任意个的任意字符
- _表示匹配一个的任意字符
// 查询所有title以v开头 使用% 表示你后面有多少个我都不关心
select * from users where title like 'v%';
// 查询所有title有v就行
select * from users where title like '%v%';
// 查询所有title第三个字符必须是v
select * from users where title like '__v%';
排序
- 当我们查询到结果的时候,我们希望讲结果按照某种方式进行排序,这个时候使用的是ORDER BY
- ORDER BY有两个常用的值
- ASC:升序排列
- DESC:降序排列
// 查询价格大于3000的手机,并按照评分降序返回结果
select * from phone where price > 3000 order by score desc
分页查询
- 当数据库中的数据非常多时,一次性查询到所有的结果进行显示是不太现实的
- 在真实开发中,我们都会要求用户传入offset、limit或者page等字段
- 它们的目的是让我们可以在数据库中进行分页查询
- 它的用法有
[LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}]
//直接查询20条数据(就是从第1条到第20条)
select * from phone limit 20
//偏移10条数据后查询20条数据(就是从第11条到第30条)
select * from phone limit 20 offset 10
//另一种写法,不推荐
select * from phone limit 10, 20
插入
//插入的数据
const user = {username:'王五',password:'789'}
const sqlStr = 'insert into users (username,password) values (?,?)' //在js中,sql可以用?来表示占位符
db.query(sqlStr,[user.username,user.password],(err,result)=>{
if(err)
return console.log(err.message)
if(result.affectedRows === 1) //插入语句,result返回值是一个对象
console.log("新增数据成功!")
})
简便写法:向表中新增数据时,如果数据对象的每个属性和数据表的字段一一对应,则可以通过如下方式快速插入数据:
const user = {username:'刘六',password:'000'}
const sqlStr = 'insert into users set ?'
db.query(sqlStr,user,(err,result)=>{
if(err)
return console.log(err.message)
if(result.affectedRows === 1) //插入语句,result返回值是一个对象
console.log("新增数据成功!")
})
更新
//更新的数据
const user = {id:2,username:'李四',password:'911'}
const sqlStr = 'update users set username = ?,password = ? where id = ?'
db.query(sqlStr,[user.username,user.password,user.id],(err,result)=>{
if(err)
return console.log(err.message)
if(result.affectedRows === 1) //更新语句,result返回值是一个对象
console.log("更新数据成功!")
})
简便写法:向表中更新数据时,如果数据对象的每个属性和数据表的字段一一对应,则可以通过如下方式快速更新数据:
const user = {id:3,username:'王五',password:'119'}
const sqlStr = 'update users set ? where id = ?'
db.query(sqlStr,[user,user.id],(err,result)=>{
if(err)
return console.log(err.message)
if(result.affectedRows === 1) //更新语句,result返回值是一个对象
console.log("更新数据成功!")
})
// 扩展:当修改某一条数据时,使用最新的时间记录
alter table phone add updateTime TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
删除
const sqlStr = 'delete from users where id = ?'
db.query(sqlStr,6,(err,result)=>{
if(err){
return console.log(err.message)
}
if(result.affectedRows === 1) //删除语句,result返回值是一个对象
console.log("删除数据成功!")
})
补充
- 创建时间项并且自动更新:
ALTER TABLE 表名字 ADD COLUMN CreateTime datetime NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT ‘创建时间' - 请空数据库并重置ID:
TRUNCATE TABLE your_table_name;
聚合函数
基本使用
聚合函数表示对值的集合进行操作的组(集合)函数。
// 查询华为手机的价格
select price from phone where name = '华为'
// 获取平均价格
select AVG(price) from phone where name = '华为'
// 重命名:重命名as可以省略,可写可不写
select AVG(price) as miPrice from phone where name = '华为'
// 最高:MAX()。但其实这样查询我们是不知道我们这个最大值是对应哪个手机的,在后面学习子查询
select MAX(price) from phone
// 最低:MIN()
// 手机价格总和:
select SUM(price) from phone
// 手机个数
select SUM(*) from phone
// 保留几位小数:round(哪个 , 位数):平均值保留2位有效值
select round(AVG(price), 2) from phone where name = '华为'
Group By
事实上聚合函数相当于默认将所有的数据分成了一组
我们前面使用avg还是max等,都是将所有的结果看成一组来计算的;
那么如果我们希望划分多个组:比如华为、苹果、小米等手机分别的平均价格,应该怎么来做呢?
这个时候我们可以使用GROUP BY;
GROUP BY通常和聚合函数一起使用:表示我们先对数据进行分组,再对每一组数据,进行聚合函数的计算
// 根据品牌进行划分,并查询有哪些分组
select brand from phone group by brand
// 根据品牌进行划分,并查询有哪些分组,每组价格最高的
select brand, MAX(price) from phone group by brand
- 对group by 之后的数据进行条件查询,我们不使用where,使用having
select brand, MAX(price) maxPrice from phone group by brand having maxPrice < 3000
多表
创建外键

外键存在时更新/删除数据

多表查询
直接从两张表查询数据:
select * from products, brands【但是这样查询出来的数据是 X * Y条】先查询后过滤:
select * from products, brands where products.id = brands.id【但是当我们某个表没有id1的时候,数据也不会展示,这也不是我们想要的】事实上我们想要的效果并不是这样的,而且表中的某些特定的数据这个时候我们可以使用SQL JOIN操作
左连接
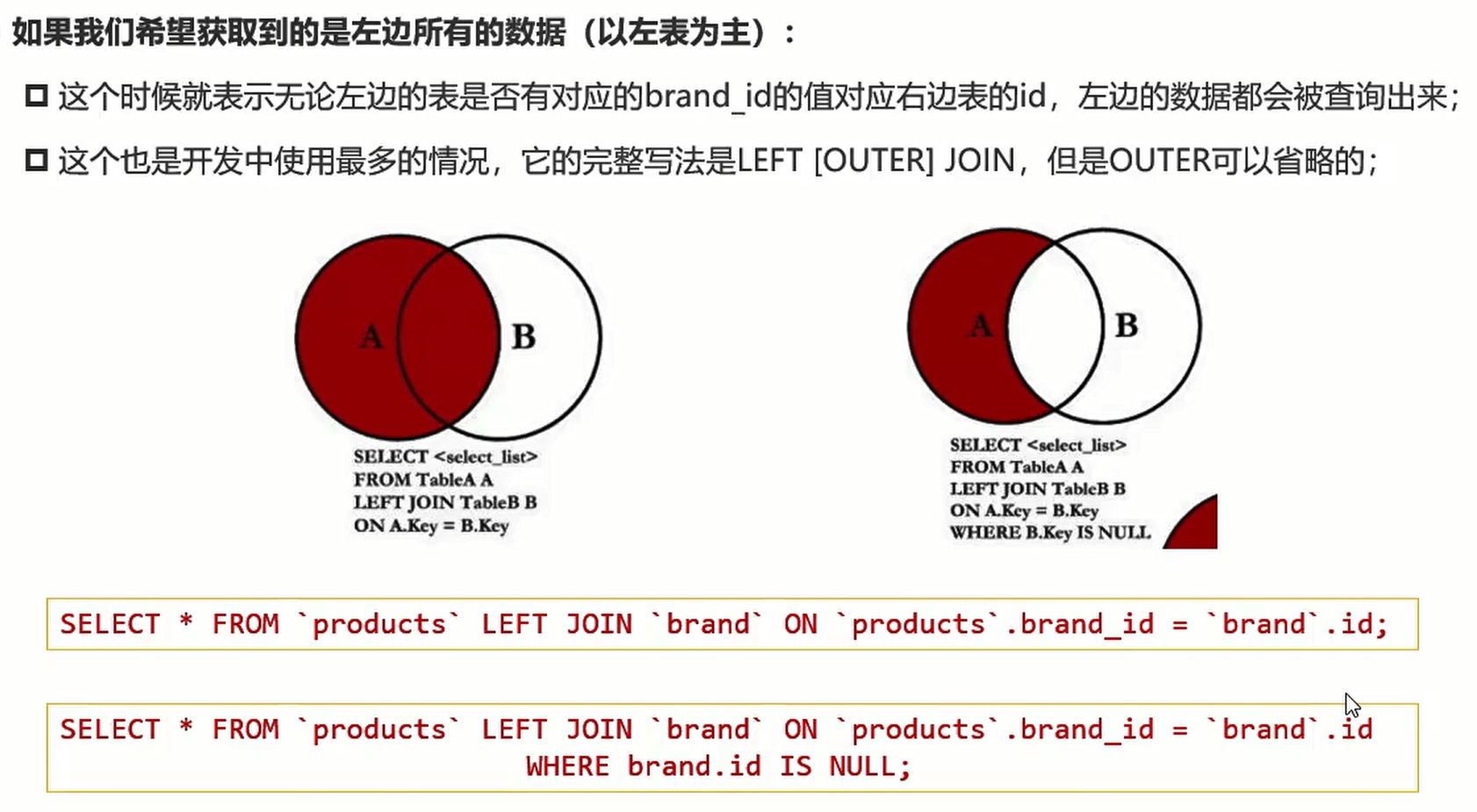
- 如果我们希望获取到的是左边所有的数据(以左表为主):
- 这个时候就表示无论左边的表是否有对应的brand_id的值对应右边表的id,左边的数据都会被查询出来
- 这个也是开发中使用最多的情况,它的完整写法是LEFT [OUTER] JOIN,但是OUTER可以省略的
-- 左连接 left join ‘表’ on 连接条件
select * from products left join 'brands' on products.id = brands.id
右连接
使用RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN
内连接
内连接是表示左边的表和右边的表都有对应的数据关联
写法:cross join 或 join 都可以
其结果和这个是一样的
select * from products, brands where products.id = brands.id
全连接

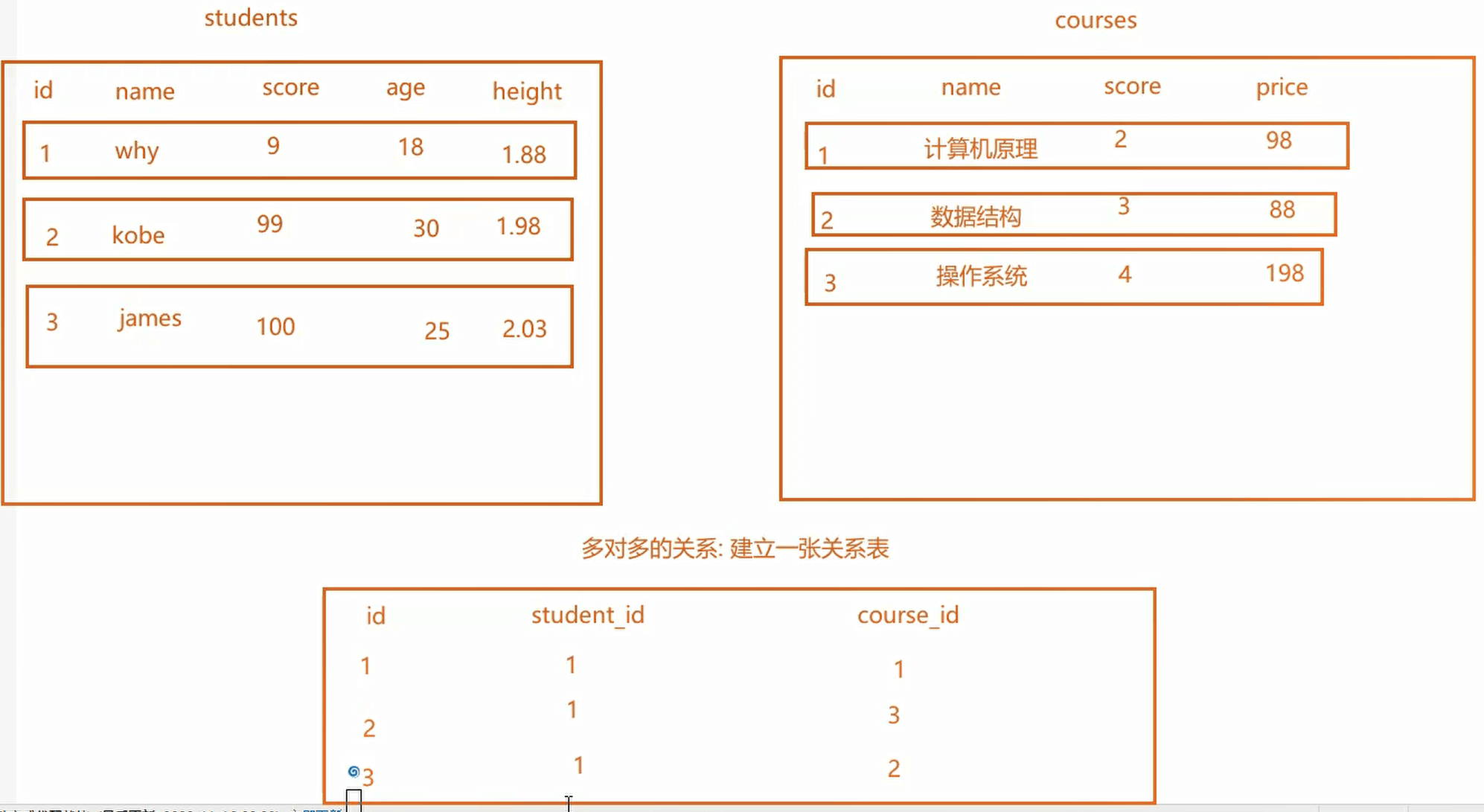
多对多的表结构
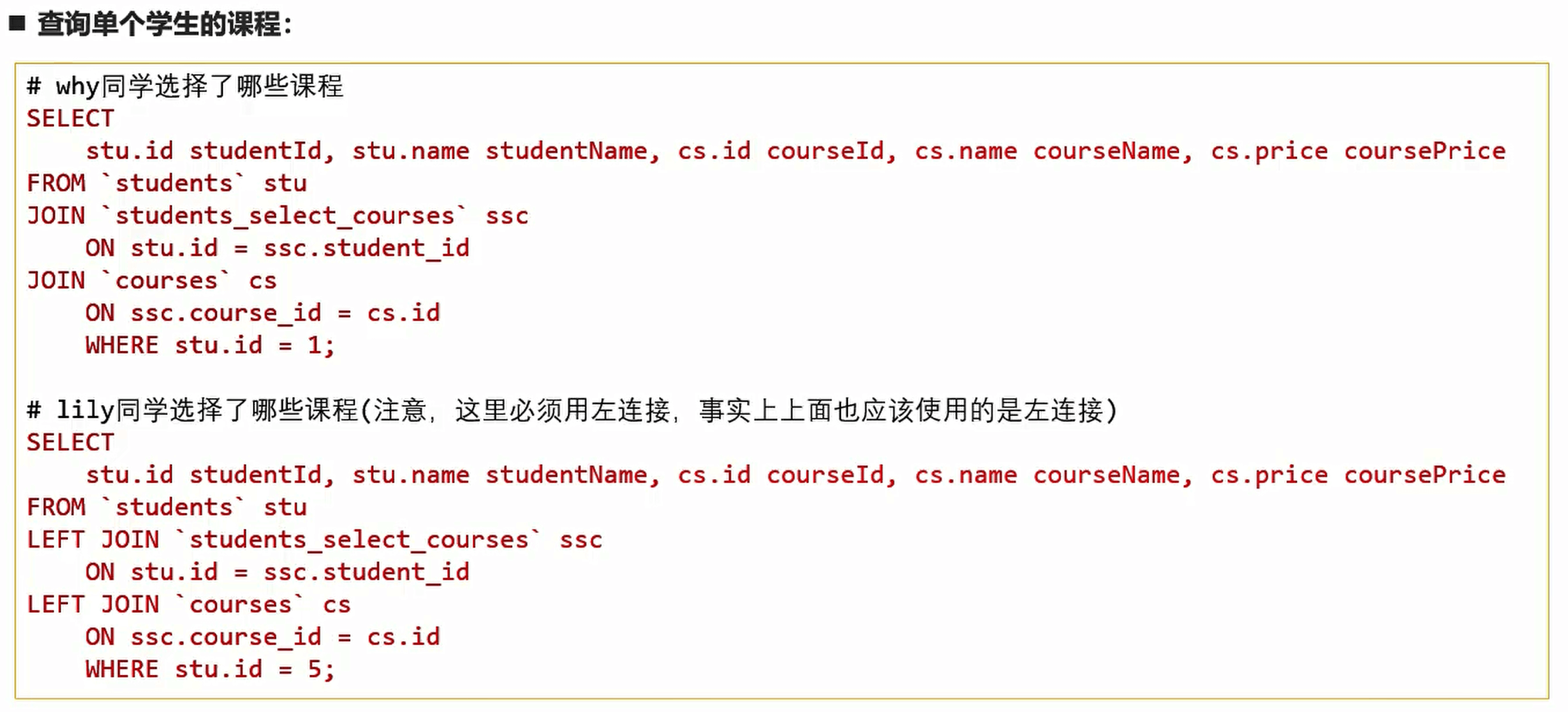
查询操作

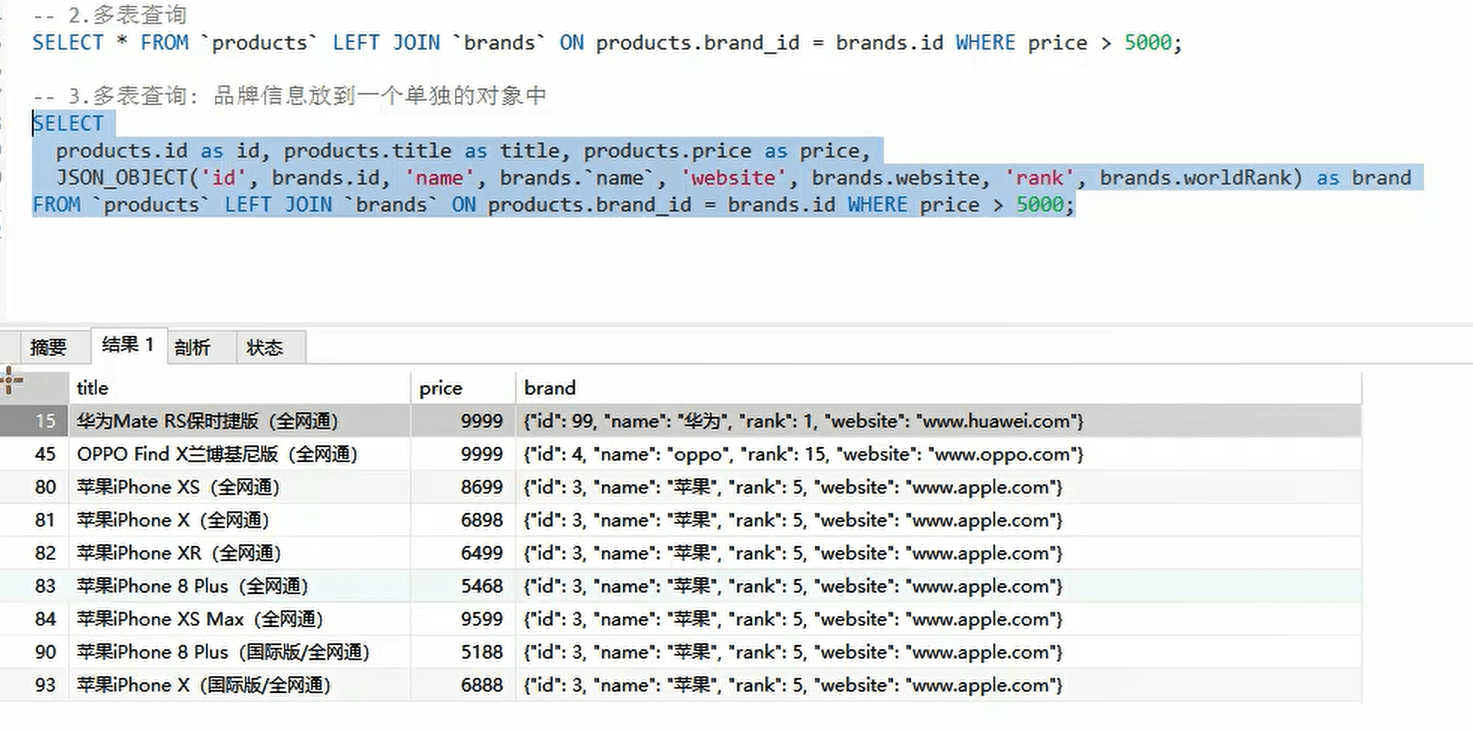
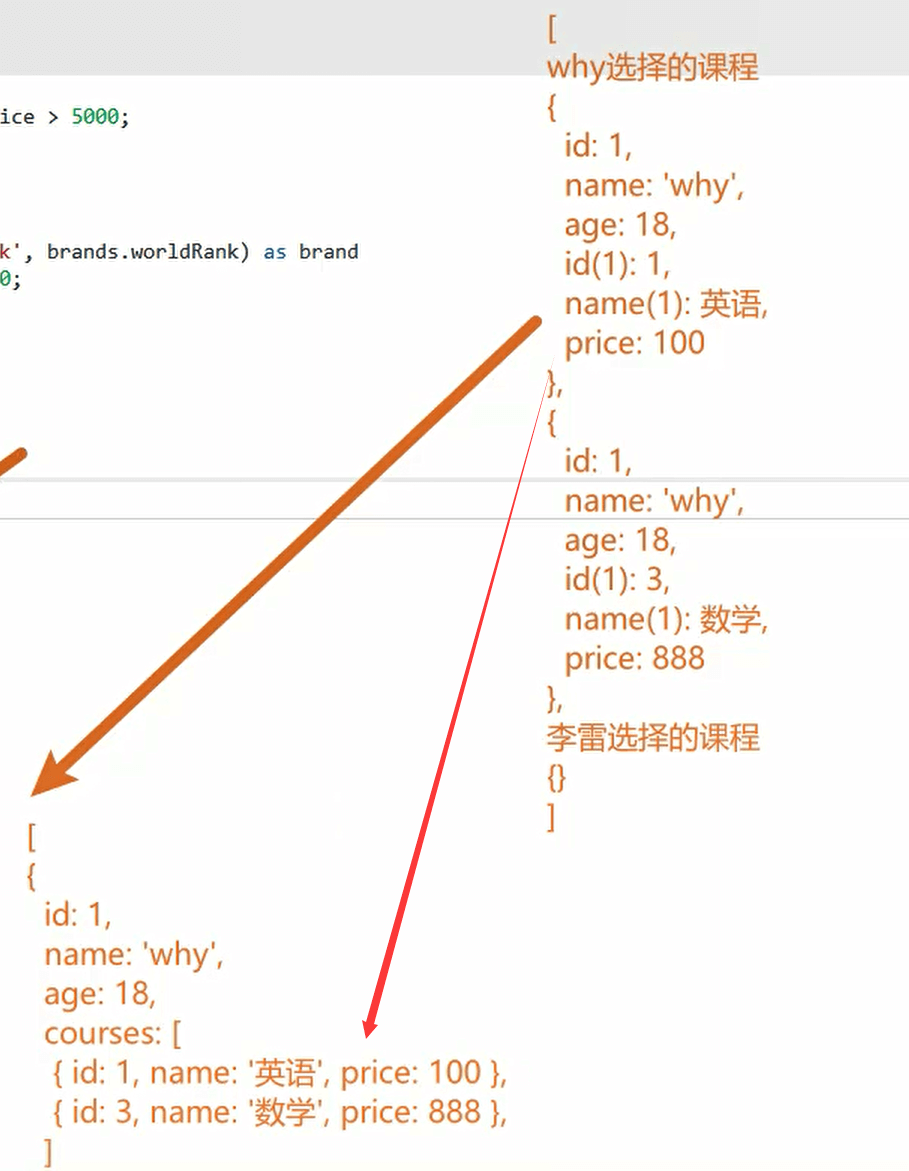
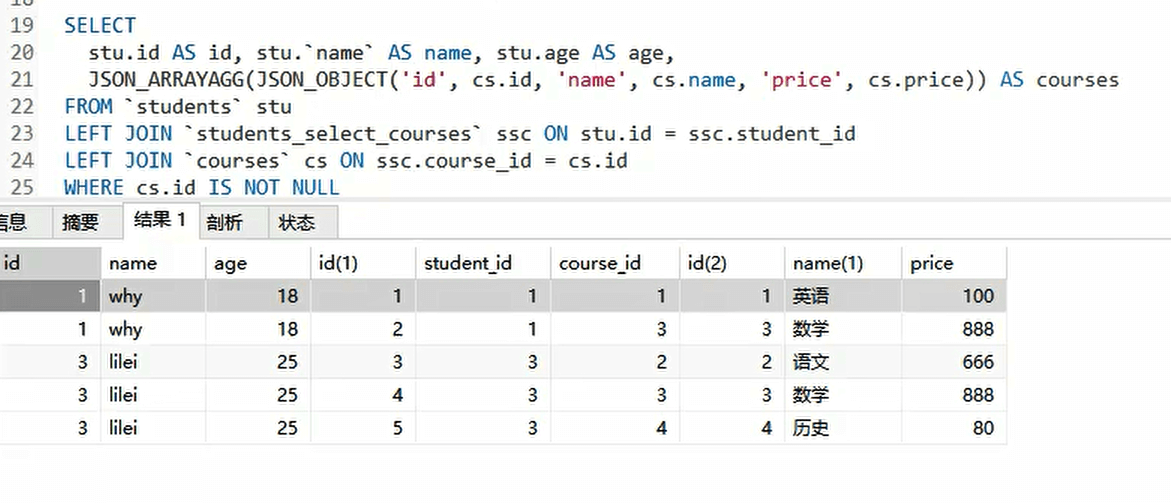
多表查询 - 对象类型
不应该将所有的数据放在一个对象里,应该一个对象包含一个对象
多表查询 - 数组类型
查询结果转为数组,数组中存放对象类型
在node中操作数据库
- 如何可以在Node的代码中执行SQL语句来,这里我们可以借助于两个库
- mysql:最早的Node连接MySQL的数据库驱动;
- mysql2:在mysql的基础之上,进行了很多的优化、改进;
- 目前相对来说,更偏向于使用mysql2,mysq2兼容mysql的API,并且提供了一些附加功能
- 更快/更好的性能
- Prepared Statement(预编译语句)
- 支持Promise,所以我们可以使用async和await语法
- 等等
基本使用
- 安装操作MySQL数据库的第三方模块(mysql2):
npm install mysql2【mysql好久不维护了】 - 通过mysql模块连接到MySQL 数据库
//1.导入mysql模块
const mysql = require('mysql2')
//2.建立与MySQL数据库的连接
const db = mysql.createConnection({
host:'localhost',//数据库的IP地址
user:'root',//登录数据库的账号
password:'123456',//登录数据库的密码
database:'teacher',//指定要操作哪个数据库
})
- 测试mysql模块是否正常工作
//调用db.query()函数,指定要执行的sql语句,通过回调拿到执行的结果【成功err默认为null】
db.query('select * from userteacher',(err,result)=>{
if(err){
return console.log(err.message)
}
console.log(result)
})
- 通过mysql模块执行SQL语句
预处理语句
const mysql = require('mysql2')
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host:'localhost',
user:'root',
password:'123456',
database:'teacher',
})
// 执行sql语句:预处理语句
const statement = 'select * from userteacher where age > ? and price < ?'
connection.execute(statement, [20, 3000], (err, values) =>{
console.log(values);
})
//销毁
connection.destroy()
连接池
- 前面我们是创建了一个连接(connection),但是如果我们有多个请求的话,该连接很有可能正在被占用,那么我们是否需要每次一个请求都去创建一个新的连接呢?
- 事实上,mysql2给我们提供了连接池(connection pools) ;
- 连接池可以在需要的时候自动创建连接,并且创建的连接不会被销毁,会放到连接池中,后续可以继续使用
- 我们可以在创建连接池的时候设置LIMIT,也就是最大创建个数
const mysql = require('mysql2')
const connectionPool = mysql.createPool({
host:'localhost',
user:'root',
password:'123456',
database:'teacher',
connectionLimit:5,//最大创建个数
})
// 执行sql语句:预处理语句
const statement = 'select * from userteacher where age > ? and price < ?'
connectionPool.execute(statement, [20, 3000], (err, values) =>{
console.log(values);
})
回调promise
也可以使用async和await
const statement = 'select * from userteacher where age > ? && price < ?'
//[values, fileds]:数组解构,res有两个数组,fileds是数据库字段
connectionPool.promise().execute(statement, [30, 3000]).then(([values, fileds])=>{
console.log(values);
}).catch((err)=>{
console.log(err);
})