栈与队列
理论知识
队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出。
用栈实现队列
https://programmercarl.com/0232.%E7%94%A8%E6%A0%88%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97.html
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/
思路
使用栈来模拟队列的行为,如果仅仅用一个栈,是一定不行的,所以需要两个栈一个输入栈,一个输出栈,这里要注意输入栈和输出栈的关系。
下面动画模拟以下队列的执行过程:
执行语句:
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.pop(); **注意此时的输出栈的操作**
queue.push(3);
queue.push(4);
queue.pop();
queue.pop();**注意此时的输出栈的操作**
queue.pop();
queue.empty();
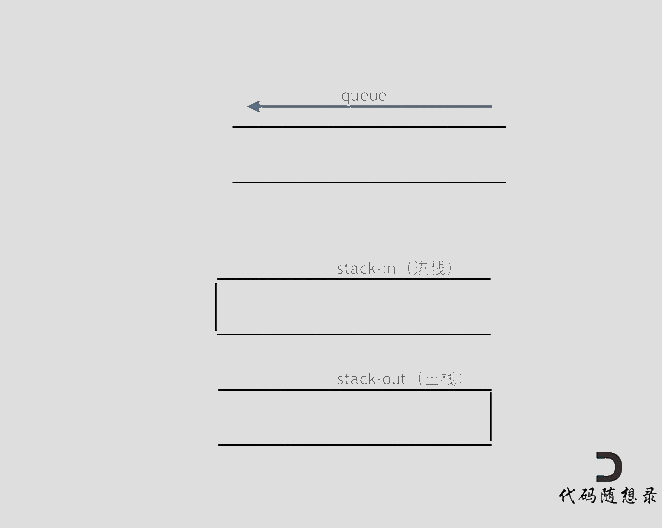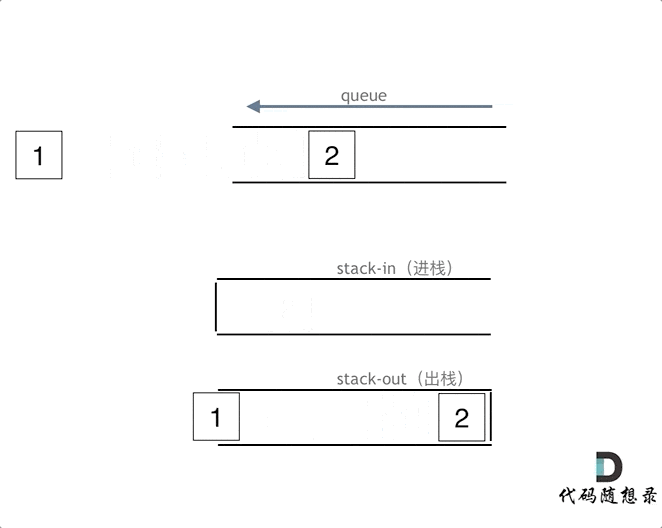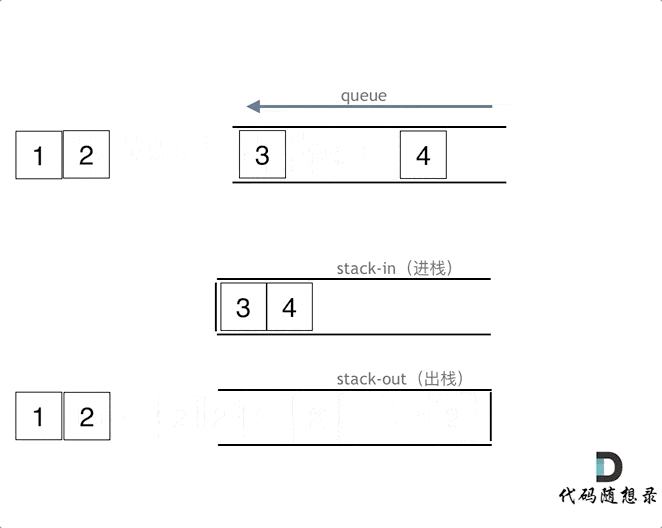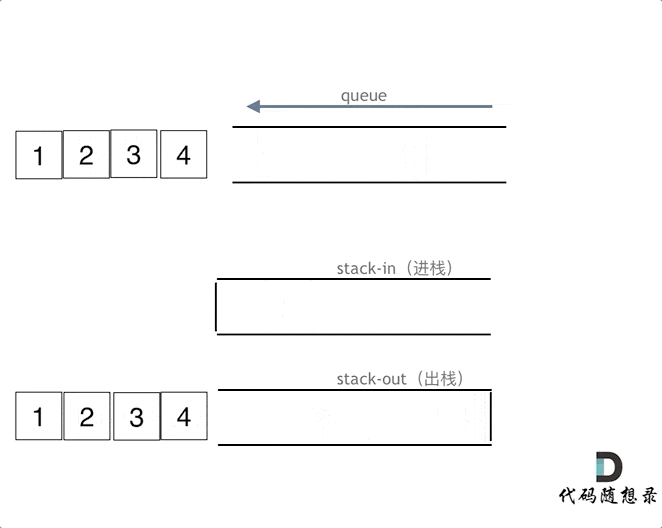
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
最后如何判断队列为空呢?如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
代码
var MyQueue = function() {
this.inArr = []
this.outArr = []
};
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.inArr.push(x)
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function() {
const n = this.outArr.length
if(n){
return this.outArr.pop()
}
while(this.inArr.length){
this.outArr.push(this.inArr.pop())
}
return this.outArr.pop()
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function() {
const x = this.pop()
this.outArr.push(x)
return x
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.outArr.length && !this.inArr.length
};
用队列实现栈
https://programmercarl.com/0225.%E7%94%A8%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E6%A0%88.html
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/
思路
其实这道题目就是用一个队列就够了。
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
代码
var MyStack = function() {
this.arr = []
};
/**
* @param {number} x
* @return {void}
*/
MyStack.prototype.push = function(x) {
this.arr.unshift(x)
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.pop = function() {
let n = this.arr.length - 1
while(n){
this.push(this.arr.shift())
n--
}
return this.arr.shift()
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyStack.prototype.top = function() {
return this.arr[0]
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyStack.prototype.empty = function() {
return !this.arr.length
};
有效括号
https://programmercarl.com/0020.%E6%9C%89%E6%95%88%E7%9A%84%E6%8B%AC%E5%8F%B7.html
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/description/
思路
代码
var isValid = function (s) {
const stack = [];
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
let c = s[i];
switch (c) {
case '(':
stack.push(')');
break;
case '[':
stack.push(']');
break;
case '{':
stack.push('}');
break;
default:
if (c !== stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
};
删除字符串中的所有相邻的重复项
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string/description/
思路
代码
var removeDuplicates = function(s) {
let arr = []
for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++){
const a = arr[arr.length - 1]
if(a === s[i]){
arr.pop()
}else{
arr.push(s[i])
}
}
return arr.join("")
};
逆波兰表达式求值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/description/
思路
逆波兰表达式是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指算符写在后面。
- 平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如
( 1 + 2 ) * ( 3 + 4 )。 - 该算式的逆波兰表达式写法为
( ( 1 2 + ) ( 3 4 + ) * )。
逆波兰表达式主要有以下两个优点:
- 去掉括号后表达式无歧义,上式即便写成
1 2 + 3 4 + *也可以依据次序计算出正确结果。 - 适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中
代码
var evalRPN = function(tokens) {
const arr = []
for(let i = 0;i<tokens.length;i++){
if( ["+", "-", "*", "/"].includes(tokens[i]) ){
const a = arr.pop()
const b = arr.pop()
let result;
switch(tokens[i]) {
case "+":
result = b + a;
break;
case "-":
result = b - a;
break;
case "*":
result = b * a;
break;
case "/":
// 注意点:正数和负数向零阶段是不一样的
result = b / a > 0 ? Math.floor(b / a) : Math.ceil(b / a);
break;
}
arr.push(result);
}else{
arr.push(Number(tokens[i]))
}
}
return arr[0]
};
result = b / a > 0 ? Math.floor(b / a) : Math.ceil(b / a) 我们可以使用 result = b / a | 0
解释:使用了按位或运算符 | 来实现取整(截断)
举个例子说明:
console.log(5 / 2); // 2.5
console.log(5 / 2 | 0); // 2(向 0 截断)
console.log(-5 / 2); // -2.5
console.log(-5 / 2 | 0); // -2(仍然向 0 截断)
注意事项:
| 0只适用于整数范围内的运算。- 对于非常大的浮点数,它可能会失去精度。
滑动窗口最大值
https://programmercarl.com/0239.%E6%BB%91%E5%8A%A8%E7%AA%97%E5%8F%A3%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E5%80%BC.html
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/description/
代码
思路
首先暴力解法是不行的,超出时间限制
然后这是我最开始的思路
var maxSlidingWindow = function(nums, k) {
const n = nums.length
if( n <= 1) return nums
if(n <= k) return [ getMaxValue(nums) ]
const arr = []
for(let i = 0; i < k;i++){
arr.push(nums[i])
}
const newArr = [getMaxValue(arr)]
for(let i = k; i < nums.length;i++){
arr.push(nums[i])
arr.shift()
newArr.push(getMaxValue(arr))
}
return newArr
};
function getMaxValue(arr){
return Math.max(...arr)
}
代码是没有问题的,但是还是超出时间限制,整个算法是 O((n - k + 1) * k)
思路:为了保证队列头部始终是当前窗口的最大值下标。
var maxSlidingWindow = function(nums, k) {
// 存储的是下标
const deque = []
// 存放最大值
const result = []
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 判断队头的元素(最左边的下标)是否已经滑出窗口
// 如果 deque[0] <= i - k,说明该元素已经不在当前窗口范围 [i - k + 1, i] 中了,需将其移除
if (deque.length && deque[0] <= i - k) {
deque.shift()
}
// 这个循环做两件事:
// 保证 deque 中的下标对应的 nums 值是从大到小的顺序
// 如果当前值 nums[i] 更大,说明前面的元素不可能是窗口最大值了,可以直接弹出
while (deque.length && nums[deque[deque.length - 1]] < nums[i]) {
deque.pop()
}
// 将当前下标加入队列
deque.push(i)
// 当窗口形成(即 i >= k - 1),将当前窗口的最大值(即队头的元素)加入结果数组。
if (i >= k - 1) {
result.push(nums[deque[0]])
}
}
return result
}
如果 deque[0] <= i - k,说明该元素已经不在当前窗口范围 [i - k + 1, i] 中了nums[deque[deque.length - 1]] < nums[i]前 K 个高频元素
https://programmercarl.com/0347.%E5%89%8DK%E4%B8%AA%E9%AB%98%E9%A2%91%E5%85%83%E7%B4%A0.html
https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/description/
思路
哈希表 + 排序
function topKFrequent(nums, k) {
const freqMap = new Map();
// 1. 统计频率
for (const num of nums) {
freqMap.set(num, (freqMap.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
// 2. 把频率映射转为数组并按频率排序
const sorted = Array.from(freqMap.entries())
.sort((a, b) => b[1] - a[1]); // 按照频率降序排序
// 3. 提取前 k 个元素的 key
return sorted.slice(0, k).map(item => item[0]);
}
哈希表 + 最小堆
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
// 插入元素
push(item) {
this.heap.push(item);
this._bubbleUp();
}
// 移除堆顶
pop() {
const top = this.heap[0];
const bottom = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = bottom;
this._sinkDown(0);
}
return top;
}
// 返回堆顶元素
peek() {
return this.heap[0];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
_bubbleUp() {
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
const element = this.heap[index];
while (index > 0) {
let parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
let parent = this.heap[parentIndex];
if (element[1] >= parent[1]) break;
this.heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
}
this.heap[index] = element;
}
_sinkDown(index) {
const length = this.heap.length;
const element = this.heap[index];
while (true) {
let leftIdx = 2 * index + 1;
let rightIdx = 2 * index + 2;
let smallest = index;
if (leftIdx < length && this.heap[leftIdx][1] < this.heap[smallest][1]) {
smallest = leftIdx;
}
if (rightIdx < length && this.heap[rightIdx][1] < this.heap[smallest][1]) {
smallest = rightIdx;
}
if (smallest === index) break;
[this.heap[index], this.heap[smallest]] = [this.heap[smallest], this.heap[index]];
index = smallest;
}
}
}
// 主函数
function topKFrequent(nums, k) {
const freqMap = new Map();
// 1. 统计频率
for (const num of nums) {
freqMap.set(num, (freqMap.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
// 2. 使用最小堆维护前 k 个频率最高的元素
const heap = new MinHeap();
for (const [num, freq] of freqMap.entries()) {
heap.push([num, freq]);
if (heap.size() > k) {
heap.pop();
}
}
// 3. 提取堆中元素
const result = [];
while (heap.size() > 0) {
result.push(heap.pop()[0]);
}
return result.reverse(); // 因为堆是最小堆,输出时反转
}